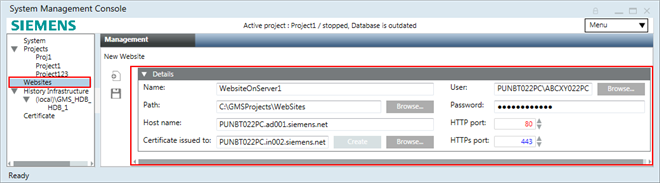
Details Expander
The Details expander allows you to create and configure a website. It also allows you to create a self-signed certificate and configure it in the website and set it as default for further use.
Item | Description |
Name | Allows you to add the name of the website you are creating. The name also appears in the tree of the IIS Manager. NOTE: The website name must be a unique name. You cannot have sites in IIS with the same name. Following special characters are not permitted in the website name: \\', '/', '?', ';', ':', '@', '&', '=', '+', '$', ',', '|', ' " ', '<', '>'. |
Path | Displays the default path for creating the website on the disk: [installation drive:]\[installation folder]\Websites. You can change this path using Browse. Following special characters are not permitted in the website path: 'ä', 'ö', 'ü', '$', '@', '<', '>', '{', '}', '[', ']', '(', ')', ';', '=', '^', '|', '*', '!', '/', '%', '?', ',', '\'', '"', '\t'. |
Host name | Full computer name, DNS name, or IP address of the Web Server (Host) system. The Host name must be available from the Web/Windows App client. |
Certificate issued to | Displays the certificate (self-signed/host) used for securing communication between the Web/Windows App client and the Web Server. By default, it displays the default self-signed certificate. There are two ways to select a self-signed certificate:
NOTE 1: This certificate is used by the Https port. NOTE 2: Ensure that the self-signed certificate you select is available in the Personal, as well as the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store of the Local machine certificates. Otherwise, a chain validity message displays. This message always displays if you use a host certificate. In this case, you should ignore it. NOTE 3: The certificate selected in this field must be the same as the host name in the Host name field. Example 1: If the host name is ABCXY022PC.dom01.company.net, and you want to use a wildcard certificate in the Issued to field of the certificate, it must be in the format *.dom01.company.net. Example 2: If you use a multi-host certificate, the certificate name can be anything, but its Subject Alternative Names must contain the host name provided in the Host name field. Example 3: If you use an SMC-created host or self-signed certificate, the certificate Subject name (issued to) should be the same as the host name provided in the Host name field. |
User | Browse for the website user from Current station or from Other Domain. It could be the local/domain user and a member of the IIS_IUSRS group. If you select a user that is not a member of the IIS_IUSRS group, the SMC prompts you to add that user to the IIS_IUSRS group. NOTE: You can use the same user when creating a Web application. In this case, the user must be assigned access rights on virtual directories (graphics, libraries, documents, shared, and devices folders) inside the Server project folder. Otherwise, the Web application user cannot work with those folders. |
Password | Type the password of the website user. |
HTTP port | Http port number. The configuration range is 80 through 65535; 80 is the default value. On a website, the HTTP port displays in red indicating that it is in use, but unsecured. For more information, see technical tips for configuring ports. |
HTTPs port | This is the port number that is used for secure communication with the Web server (for example, as file transfer). The configuration range is 443 through 65535; 443 is the default value. On a website, the HTTPs port displays in blue indicating that it is secured and must be opened in the Windows firewall. |